Slip Is Used to Describe Movements on Faults
However a transform fault is formed between two different plates each moving away from the spreading center of a divergent plate boundary. If the block opposite an observer looking across the fault moves to the right the slip style is termed right lateral.

Fold And Fault Model 13 Inch In 2022 Visual Learning Fold Model
Its length provides the amount of displacement on the fault which generally is the addition of several movements.

. The fault plane is essentially vertical and the relative slip is lateral along the plane. Elastic-rebound theory is the concept that earthquakes happen because stresses build up causing rock to bend elastically until slip on a fault occurs. Also fault strike length.
When the residual strength of the fault is exceeded an earthquake will occur. I a sideways movement called strike slip and 2 an up or down movement called dip slip. If the block on the far side of the fault moves to the left as shown in this animation the fault is called left-lateral.
Slip is defined as the relative movement of geological features present on either side of a fault plane. A dip-slip fault in which the upper block above the fault plane moves up and over the lower block. Strike-slip faults are vertical or nearly vertical fractures where the blocks have mostly moved horizontally.
A transcurrent fault if marker beds of different orientation show the same displacement across it. The direction of slip is measured on the fault surface and like the strike and dip it. Sometimes in a homogeneous body of rock the gouge thickness is used as a proxy for slip.
Describing motion that is a combination of movement both perpendicular and parallel to the strike of a fault -- a combination of strike. This strike-slip movement is described as sinistral when the far side moves to the left and dextral when the far side moves to the right. Faults which show both dip-slip and strike-slip motion are known as oblique-slip faults.
Strike-slip fault Both blocks slide horizontally across one another. Disaggregation bands can be formed by slow-slip and creep behaviour which could allow them. Thrust fault is a special kind of normal fault where the dip angle is 45 degrees.
Cataclasite is sometimes used to describe fine grained material without fabric and with rather even-size fragments. In a vertical section the fault movement is DIP-SLIP a thrust or normal fault if marker beds of different orientation show the same displacement across it. Transform faults can be distinguished from the typical strike-slip faults because the sense of movement is in the opposite direction see illustration.
A fault which has a component of dip-slip and a component of strike-slip is termed an oblique-slip fault. 100 Faults jpb 2020. Rupture along a fault typically occurs by fits and starts in a type of sporadic motion that geologists call stick-slip.
This type of faulting is common in areas of compression When the dip angle is shallow a reverse fault is often described as a thrust fault. First characterized about 10 years ago in Cascadia by Canadian scientists slow-slip motion is episodic movement across a fault that releases energy on timescales of hours to weeks rather than seconds to minutes as occurs in earthquakes. The fault motion of a strike-slip fault is caused by shearing forces.
It means movement has occurred along a fault. That is the slip occurs along the strike not up or down the dip. Strike Slip Fault Crustal blocks may also move sideways past each other usually along nearly-vertical faults.
Why is Japan subjected to powerful earthquakes. San Andreas Fault is a formed when plates move passed each other. Strike-Slip Faults Strike-slip faults occur as plates scrape by each other.
Jack0mDigitalVision VectorsGetty Images Strike-slip faults have walls that move sideways not up or down. Slip is the direction of movement of one wall relative to the other. The net slipis the displacement vector connecting originally coincident points the on opposite sides of the fault piercing points plane.
A strike-slip fault is a simple offset. Disaggregation bands could open a new path to detect hidden active faults undergoing aseismic movements. Strike-slip faults are right lateral or left lateral depending on whether the block on the opposite side of the fault from an observer has moved to the right or left.
Stick-slip behavior describes when earthquakes occur due to slip on a preexisting fault. Faults which move along the direction of the dip plane are dip-slip faults and described as either normal or reverse thrust depending on their motion. The magnitude of slip is simply how far the two sides of the fault moved relative to one another.
Faults act like scars they remain weaker than the surrounding crust. Graben is the downward block in a series of normal fault. Fault Fracture in two mats with relative movement Dip-slip Incline split with vertical movement upwards or downwards Strike-slip Straight split with horizontal movement right or left lateral Lithosphere Floating mat.
The strain axes lie in the movement plane at 45 to the fault plane and to the pole to the fault plane. In these faults the fault plane is usually vertical so there is no hanging wall or footwall. Reverse dip-slip fault usually forms when plates moves away from one another.
In a horizontal section usually called a map the fault movement is STRIKE-SLIP ie. FAULT CLASSIFICATION Faults and fault zones are classified by how the rocks on each side of the fault or fault zone move past each other There are two main types of movement along faults. Nearly all faults will have some component of both dip-slip and strike-slip so defining a fault as oblique requires both dip and strike.
What does the word slip refer to when used to describe earthquakes. Its a distance usually a few centimeters for small earthquakes and meters for large events. When stress builds up the fault slips before the stress becomes.
Occurs where the hanging wall moves up or is thrust over the foot wall. A faults sense of slip is defined as the relative motion of the rock on each side of the fault concerning the other side. Strike-slip Now you can substitute these terms.
Faults which move horizontally are known as strike-slip faults and are classified as either right-lateral or left-lateral. As energy builds up the rock on either side of the fault will store the energy until its force exceeds the strength of the fault. Synthetic and antithetic faults are terms used to describe minor faults associated with a major fault.
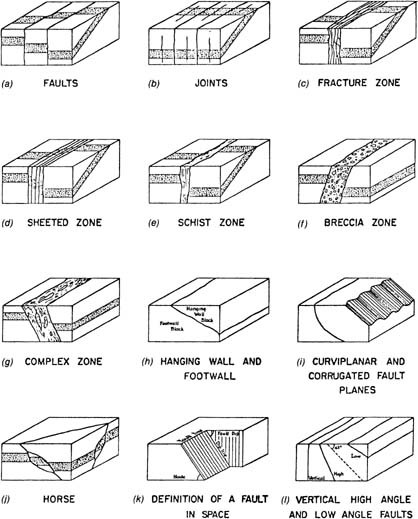
Faults And Faulting Springerlink

Geo Expro Know Your Faults Part Ii

Logic Lineup Earthquake Faults And Plateau Puzzle Normal Reverse Strike Slip Critical Thinking Skills Teamwork Skills Earthquake Fault
File Oblique Slip Fault Png Wikimedia Commons

Do You Know The Different Types Of Faults Geology Plate Tectonics Transform Boundary

Earthquake Faults 3 Basic Types In Brief Educational Youtube

1 1 Major Classes Of Strike Slip Fault In Their Plate Tectonic Setting Download Scientific Diagram

Tectonic Settings Of Strike Slip Faults And Related Strike Slip Basins Download Scientific Diagram

Fault Terminology Learning Geology Geology Teaching Geology Geography Project

It S Not My Fault Engineering Design Challenge Earth Science Rock Cycle

Earth Science Earth And Space Science Geophysics

Block Diagram Of The Strike Slip Style And Pull Apart Development Download Scientific Diagram

A An Example Of A Typical Dextral Strike Slip Fault System And The Download Scientific Diagram

A Left Lateral Strike Slip Fault Fault Types What Are The Three Main Types Of Faults Geology Page Geology Fault University Of Saskatchewan
Where And How Do Faults Occur Quora
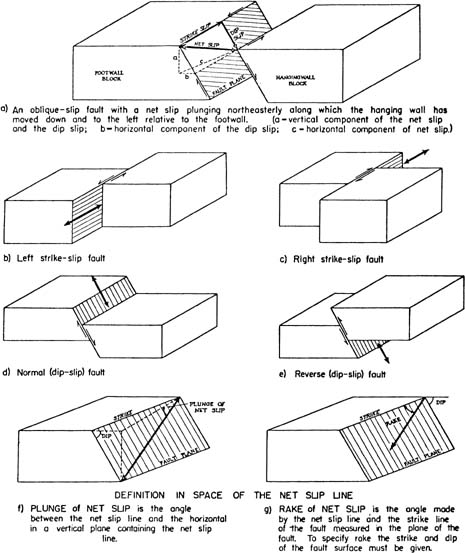
Faults And Faulting Springerlink
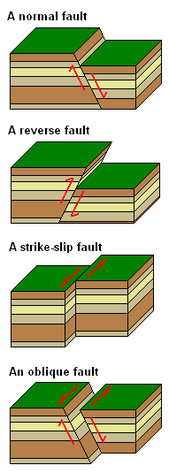
Anderson S Theory Of Faulting Wikipedia

Types Of Tectonic Faults Normal Fault Strike Slip Fault And Reverse Download Scientific Diagram

Anderson S Faulting Theory And Stress Regimes A Strike Slip Fault Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment